What is a Nebula?
What is a Nebula?
A nebula is a gigantic cloud of dust and gas found in space, often hundreds of light-years across. Some nebulae are where new stars are born, while others are the leftover remains of dead or dying stars. Nebulae come in amazing shapes and glowing colors, creating some of the most beautiful sights in the universe.
The word "nebula" comes from the Latin word for "cloud." When telescopes were first invented, anything fuzzy in the sky was called a nebula. Later, astronomers learned that some of those fuzzy objects were galaxies, while others were true clouds of gas and dust — the nebulae we study today.
How Are Nebulae Formed?
Nebulae form in several ways:
- Supernova Remnants: When a massive star explodes in a supernova, its outer layers are blasted into space, creating a glowing cloud of gas and dust.
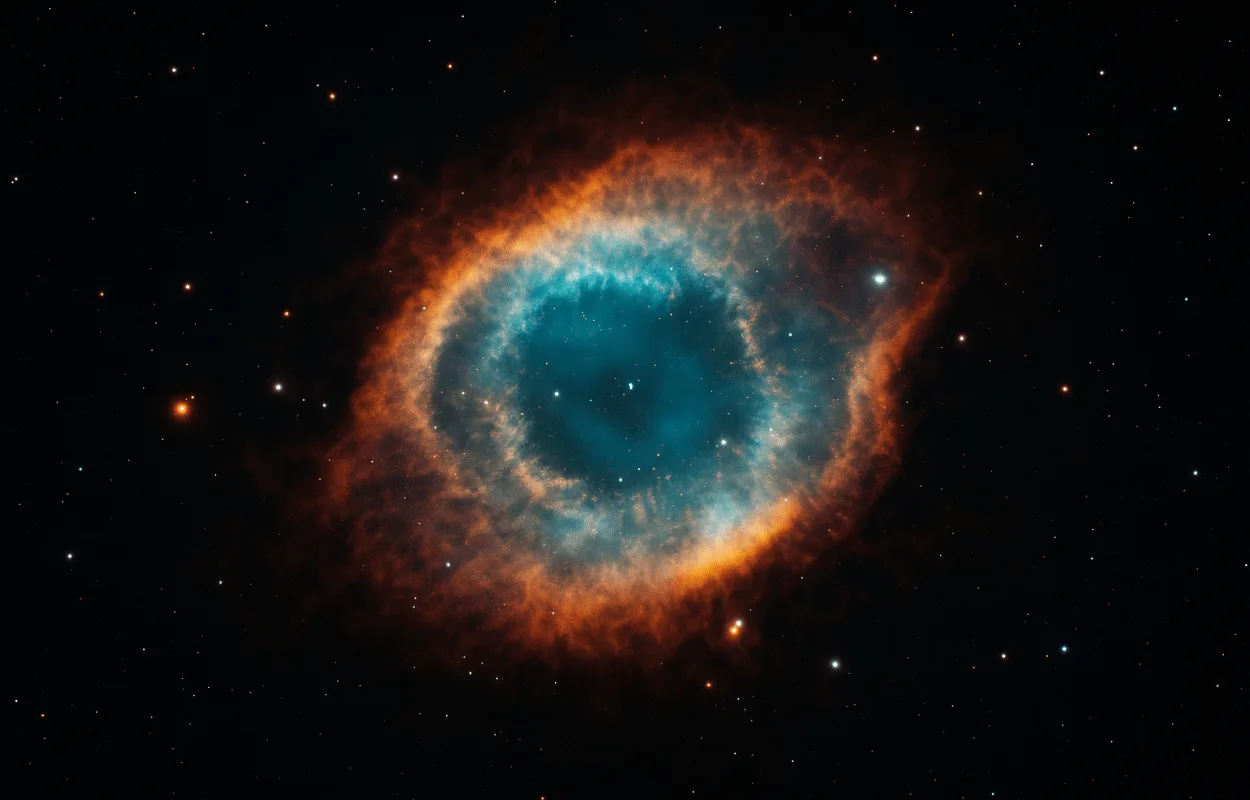
- Planetary Nebulae: When a smaller star like our Sun reaches the end of its life, it gently sheds its outer layers, creating a shell of glowing gas around a tiny leftover core called a white dwarf.
- Interstellar Clouds: Some nebulae form naturally over millions of years as regions in space collect gas and dust, pulled together by gravity.
These materials — hydrogen, helium, and tiny dust particles — eventually clump together to start forming new stars and planets.
Types of Nebulae
There are several different types of nebulae, each with unique properties:
- Emission Nebulae: These glow brightly because their gas is energized by nearby young stars. Example: Orion Nebula.
- Reflection Nebulae: These don’t glow on their own but shine by reflecting the light of nearby stars. Example: Pleiades Reflection Nebula.
- Dark Nebulae: These thick clouds of dust block light from stars behind them, appearing like dark patches against the bright background. Example: Horsehead Nebula.
- Planetary Nebulae: Created from dying stars shedding their outer layers. Example: Ring Nebula.
Why Are Nebulae Important?
Nebulae are vital for the life cycle of stars. They act as "stellar nurseries," where gas and dust gather to form new stars and planets. In a way, every star, including our Sun, was born in a nebula. Even we are connected to them — the elements in our bodies were once created inside stars that formed inside nebulae!
Nebulae also help astronomers study how stars live and die. By observing different types of nebulae, scientists understand more about the birth of solar systems, the recycling of matter in space, and the evolution of galaxies.
Famous Nebulae You Should Know
- Orion Nebula (M42): A huge, bright star-forming region located in the Orion constellation, easily visible with binoculars.
- Crab Nebula (M1): The remains of a supernova explosion observed by Chinese astronomers in 1054 AD.
- Eagle Nebula: Famous for the "Pillars of Creation," giant structures made of gas and dust where new stars are forming.
- Ring Nebula (M57): A beautiful, colorful planetary nebula that looks like a donut in the sky.
Fun Fact!
Even though nebulae seem thick and cloudy, they are actually very empty! If you were inside a nebula, you wouldn't notice anything around you — they are much less dense than even the best vacuums we can create on Earth!
You might also like

What is Gravity?
